chest compression depth for child according to aha bls test|Part 4: Pediatric Basic and Advanced Life Support : services • Ensuring chest compressions of adequate depth • Allowing full chest recoil between compressions • Minimizing interruptions in chest compressions • Avoiding excessive .
Resultado da 26 de out. de 2023 · PEDRO LOOS e GREG DE SOUZA são YouTubers. Ele são integrantes do Sinapse Podcast no Spotify, onde trocam ideia sobre ciência .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBAo continuar você estará concordando com os novos Termos de Uso do Fatal Model. Continuar Conteúdo Adulto. Entendo que o site Fatal Model apresenta conteúdo explícito destinado a adultos. Termos de uso. AVISO DE COOKIES Nós usamos cookies e outras tecnologias semelhantes para melhorar a sua experiência em nosso site. .
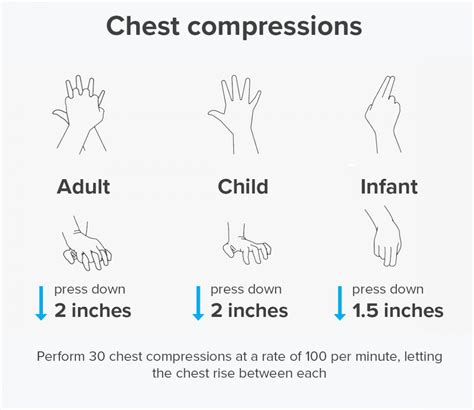
For infants and children, it is reasonable for rescuers to provide chest compressions that depress the chest at least one third the anterior-posterior diameter of the chest, which equates to approximately 1.5 inches (4 cm) in .Pediatric Basic and Advanced Life Support. High-quality CPR is the foundation of resuscitation. • Make sure you have adequate compression rate and depth. • Allow for full chest recoil. • .30 compressions and 2 breaths. • When second rescuer arrives, perform cycles of 15 compressions and 2 breaths. • Use AED as soon as it is available. • Continue rescue .
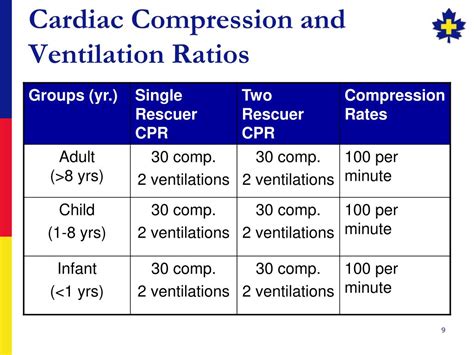
New data reaffirm the key components of high-quality CPR: providing adequate chest compression rate and depth, minimizing interruptions in CPR, allowing full chest recoil between compressions, and avoiding .The 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC recommend a CAB sequence (chest compressions, airway, breathing/ventilations). This section will review some of the rationale for making the change for children as well as for adults.• Ensuring chest compressions of adequate depth • Allowing full chest recoil between compressions • Minimizing interruptions in chest compressions • Avoiding excessive .The 2020 Guidelines use the most recent version of the AHA definitions for the COR and LOE (Figure 1). Overall, 491 specific recommendations are made for adult, pediatric, and neonatal .
providing adequate chest compression rate and depth, minimizing - inter ruptions in CPR, allowing full chest recoiand l between compressions, avoiding excessive ventilation. 2. A respiratory .
What Is the Correct Depth of Chest Compression for Infants and C
In infants and children, chest compressions are delivered at a rate of 100 to 120 per minute without pauses, and ventilations are administered at a rate of 20 to 30 breaths per . The 2020 American Heart Association (AHA) CPR guidelines recommend a 30:2 compression to ventilation ratio for infants in emergency settings. That means for every 30 chest compressions, you should provide 2 . The 2020 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiovascular Care provides a comprehensive review of evidence-based recommendations for . Update on compression depth and rate: The 2020 AHA guidelines recommended a change in compression depth for pediatric CPR. For children, the guideline emphasized a compression depth of at least 2 inches (5 .
2. Give 30 compressions. For a child, place the heel of one hand in the center of the child’s chest, with your other hand on top and your fingers interlaced and off the child’s chest . Position your shoulders directly over your hands and lock your elbows; Keep your arms straight; Push down hard and fast about 2 inches at a rate of 100 to 120 per minute
Recommended Compression to Ventilation Ratios for
%PDF-1.5 %âãÏÓ 116 0 obj > endobj xref 116 126 0000000016 00000 n 0000003337 00000 n 0000003548 00000 n 0000003592 00000 n 0000005172 00000 n 0000005199 00000 n 0000005334 00000 n 0000005469 00000 n 0000005506 00000 n 0000006046 00000 n 0000006094 00000 n 0000012100 00000 n 0000012604 00000 n 0000012945 00000 n .Start compressions within 10 seconds of recognition of cardiac arrest; Chest compression rate of 100 – 120 per minute; Compression depth of 2 – 2.4 in. (5-6 cm.) for adults and children; Compression depth of 1.5 in. (4 cm.) for infants; Minimize interruptions in compressions; Do not over-ventilate the victim
Enhance your expertise with our BLS practice test. Simulating real emergencies, it covers airway management, cardiovascular, and respiratory treatment . Give an adult or child 30 chest compressions before the two rescue breaths and an infant 15 chest compressions before the two rescue breaths. The depth of compressions for an adult is 2 to 2. .
Emerging evidence in adult victims of cardiac arrest suggests that the provision of longer sequences of uninterrupted chest compressions (a compression-ventilation ratio >5:1) may be easier to teach and retain. 61 133 In addition, animal data suggests that longer sequences of uninterrupted chest compressions may improve coronary perfusion. 247 . Neither study identified a difference in chest compression depth between groups: Backboard use: Low (serious indirectness) Six manikin RCTs (meta-analyzed) 90,93–97: 221: Improved chest compression depth: mean difference 2.74 mm (95% CI, 1.19 to 4.28) One manikin RCT* 98: 24: No difference in chest compression depth between groups *
The American Heart Association is pleased to announce that the official 2020 American Heart Association Guidelines for CPR & Emergency Cardiovascular Care (2020 AHA Guidelines for CPR & ECC) will be published online in the AHA’s flagship journal, Circulation, on Wednesday, October 21, 2020.Rescuer 1: Infant Compressions ☐ Performs high-quality compressions*: • 15 compressions with 2 thumb–encircling hands technique • 15 compressions in no less than 7 and no more than 9 seconds • Compresses at least one third the depth of the chest, approximately 1½ inches (4 cm) • Complete recoil after each compressionThe recommended chest compression depth for adults is 2 to 2.4 inches (5-6cm). Since 2015, the American Heart Association has updated the CPR guidelines. As a result, the chest compression depth for adults has changed from 2 inches to 2 to 2.4 inches deep.
is the mn post test hard
2020 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Pediatrics. 2020; doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-038505D ©2020 American Heart Association, Inc. Reprinted with permission of the American Heart Association, Inc. This article has been published in . Circulation. THE AMERICAN Heart Association (AHA) recently released updated guidelines for advanced cardiovascular life support (ACLS), basic life support (BLS), and pediatric advanced life support (PALS) for in- and out-of-hospital responses from both healthcare professionals and nonprofessionals.
*This guide is based on the American Heart Association 2020 guidelines. Always check to make sure you are using the most up-to-date science, as the guidelines change roughly every 5 years! . Compression depth: The compression depth refers to the desired amount that rescuers should press down on the patient’s chest during chest compressions .Standing to the side of the infant, place two fingers of your hand closest to the infant's feet in the center of the exposed chest, just below the nipple line on the sternum. Then provide 30 chest compressions. Compress to about 1½ inches deep at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute. As you do this, allow for complete chest recoil.The recommended compression depth and rate have also evolved to optimize blood flow during CPR. The current guidelines stress the importance of delivering chest compressions with a depth of at least 2 inches (5 centimeters) and up .
chest compression depth at least one third the anterior-posterior diameter of the chest, or by 4 cm for the infant and 5 cm for the child. chest compression pauses minimised so that 80% or more of the CPR cycle is comprised of .Press at least to 1/3 the depth of patient’s chest or 2 inches. Press hard and fast. Allow for full chest recoil with each compression. Allow for only minimal interruptions to chest compressions. (One Provider: 1 cycle is 30 chest compressions to 2 rescue breaths) (Two Providers: 1 cycle is 15 chest compressions to 2 rescue breaths) A case series of 6 infants with heart disease examined blood pressure during CPR in relation to chest compression depth and observed a higher systolic blood pressure during CPR in association with efforts to increase chest compression depth. 17 Another report of 87 pediatric resuscitation events, most involving children older than 8 years .Single Hand CPR for Children. During CPR on a child, you should place 1 or 2 hands in the center of the child's chest, between the nipples.If you become tired during compressions, use both hands to ensure you continue to reach the desired depth at .
is the montana drivers test hard
Our standardized and objective practice test follows the latest AHA, Redcross, ASHI, ECC, and OSHA guidelines. . Give an adult or child 30 chest compressions before the two rescue breaths and an infant 15 chest compressions before the two rescue breaths. . Our Basic Life Support certification course strictly adheres to the American Heart .depth of the chest, about 2 inches. 1/3 chest depth, about 1.5 inches. 1 breath every 2-3 seconds. Assess pulse for no more than 10 seconds. Pulse under 60/minute with poor perfusion despite rescue breathing: add compressions.. Search for a pulse at the brachial artery on the upper arm. Adult/Child/Infant Adult/Child/Infant Adult/Child InfantWhat is the compression to breath ratio in two-person CPR for an adult? 20:2; 30:2; 40:2; 25:2; . Using one arm, press to 1/3 depth of chest; . BLS Algorithms 2024 (Basic Life Support) Pretest Center Toggle child menu. ACLS Pretest Questions and Answers; A. Perform rescue breaths without chest compressions. B. Perform chest compressions without rescue breaths. C. Deliver both chest compressions and rescue breaths. D. Attach the AED pads to the child’s chest and read the analysis. 9. What is the compression-to-ventilation ratio for adult CPR involving 2 rescuers? A. 5 to 1 B. 20 to 2
CPR Exam BLS 2021 AHA through Heart CPR Training Center 25 questions Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. . (When performing chest compressions on an adult (or adolescent), a compression depth of at least 2 inches (5 cm) should be used.) . (The correct compression depth for a child victim is at least one third the AP . Rescuer fatigue can lead to inadequate compression rate, depth, and recoil. 32,47,50 The quality of chest compressions may deteriorate within minutes even when the rescuer denies feeling fatigued. 51,52 Rescuers should therefore rotate the compressor role approximately every 2 minutes to prevent compressor fatigue and deterioration in quality .Provide CPR with compressions and breaths. Child CPR Push on the middle of the chest 30 times at a depth of 2 inches with 1 or 2 hands. Provide 30 compressions and then 2 breaths. Repeat cycles. Infant CPR Push on the middle of the chest 30 times at a depth of 1½ inches with 2 fingers. Provide 30 compressions and then 2 breaths. Repeat cycles.
Pediatric Basic Life Support Algorithm for Healthcare
Ângela Diniz era filha de Newton Viana Diniz e Maria do Espírito Santo Fernandes Diniz. Casou-se aos 17 anos com o engenheiro Milton Villas Boas, 31 anos, com quem teve três filhos. O relacionamento durou apenas 9 anos e, quando terminou, o casal fez um acordo judicial de desquite, já que o divórcio não era permitido à época. No acordo, Ângela recebeu uma pensão mensal e uma mansão em Belo Horizonte, porém, a guarda dos três filhos ficou com Milton.
chest compression depth for child according to aha bls test|Part 4: Pediatric Basic and Advanced Life Support